brownish sedge
(Carex brunnescens ssp. brunnescens)
Conservation • Wetland • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Use • Distribution • Taxonomy
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Description |
Brownish sedge (ssp. brunnescens) is a perennial, medium sized, true sedge. It is native to northern Europe and the northern forested regions of North America. Brownish sedge (ssp. brunnescens) is found in a variety of wet, moist, and temporarily dry habitats. It grows in both shaded and exposed areas. It is found in forested peatlands; swampy or boggy areas (mires) with a thin layer of peat; thickets; moderately moist mixed forests; moist, shallow, natural or man-made channels (swales) in woodlands; and moist areas in rock outcrops. Brownish sedge (ssp. brunnescens) is forms small, very dense clumps. It rises from underground, horizontal stems (rhizomes). The rhizomes are slender and short, no more than 2″ (5 cm) long and sometimes too short to be recognized as rhizomes. Within the tuft, each individual plant has a single, unbranched, flowering stem with a cluster of leaves at the base. The flowering stem (culm) is three-angled, slender, usually erect but sometimes nodding, 6″ to 24″ (15 to 60 cm) tall, and brown at the base. It is usually longer than the leaves. The leaves are restricted to the lower half of the culm. The lower part of each leaf that surrounds the culm (sheath) is tight around the culm and is pale brown or medium brown. The front of the sheath is thin and more or less transparent (membranous). The tip is concave. The inner band is thin and translucent. The membrane where the leaf meets the culm (ligule) is as long as wide. Each blade is usually 4″ to 10″ (10 to 25 cm) long, sometimes up to 15¾″ (40 cm) long, and usually 1⁄16″ to ⅛″ (1.5 to 2.5 mm) wide, sometimes only 1⁄32″ (1.0 mm) wide. When young, it is V-shaped in cross section. When mature, it is flat, hairless, and medium green to yellowish green or grayish green. The lowest leaves are reduced to bladeless or almost bladeless sheaths, and they are called basal sheaths. The basal sheaths are pale brown and fibrous. They usually do not last for more than a year. The inflorescence is a usually erect, sometimes nodding, usually ⅝″ to 2″ (1.5 to 5.0 cm) long, sometimes up to 2¾″ (7 cm) long, ⅛″ to ¼″ (3 to 6 mm) wide, unbranched cluster (raceme) of 5 to 10 groups of flowers (spikes) at the end of the culm. The two spikes at the tip are closely spaced, the remaining spikes are widely separated. The middle and lower spikes are 3⁄16″ to 1″ (5 to 25 mm) apart. Each spike is stalkless and is subtended by a single modified leaf (bract). The lowest bract is stiff, bristle-like, and long, up to 1 9⁄16″ (4 cm) in length, but it is not longer than the inflorescence. Each spike is globe-shaped or slightly longer than wide, ⅛″ to ¼″ (3 to 7 mm) long, and ⅛″ wide. It usually has 5 to 10 female (pistillate) flowers, but it may have up to 15 or even more. The terminal spike has both male and female flowers, with pistillate (female) flowers at the tip and staminate (male) flowers at the base. It is ellipse shaped or almost club shaped, with a narrow staminate base that is not quite as long as the pistillate portion above. Each pistillate flower is entirely enclosed by a sac-like bract (perigynium) and subtended by a single scale. The scale is egg-shaped and has a pointed tip. It is shorter than the perigynium. It is translucent (hyaline) white on the sides and green with 3 veins in the center. The perigynium is elliptic or slightly egg-shaped, 1⁄16″ to ⅛″ (2.0 to 2.5 mm) long, and 1⁄32″ to 1⁄16″ (1.0 to 1.5 mm) wide. It may be green or brown. The upper side is convex with indistinct veins, the underside is flat and usually has no veins. The perigynia are appressed and ascending when young and loosely spreading when mature. It often becomes dark brown with old age. The extended tip (beak) is flat and short, 1⁄128″ to 3⁄128″ (0.2 to 0.6 mm) long. The margins are minutely toothed. Two white stigmas emerge from a small opening at the tip of the perigynium. The fruit is a dry, pale brown to medium brown, egg-shaped to almost circular, one-seeded capsule (achene). It is 1⁄32″to 1⁄16″ (1.25 to 1.5 mm) long and 1⁄32″ (0.8 to 1.0 mm) wide, much smaller than the perigynium. The style drops off the achene as it matures, which is from early June to early August. In open sunny areas, the culm is stiff and the scales are strongly tinged brown. In shady areas, the culms are more slender and weaker, and the scales take on little or no brown color. |
Height |
6″ to 24″ (15 to 60 cm) |
Similar Species |
Round-spike brownish sedge (Carex brunnescens ssp. sphaerostachya) is a taller plant. The culms are ascending or arching and 12″ to 36″ (30 to 90 cm) tall. The leaf blade is green to dark green and usually 1⁄32″ to 1⁄16″ (1.0 to 1.5 mm) wide, sometimes only 1⁄64″ (0.5 mm) wide. The inflorescence is a flexible, usually ⅝″ to 1½″ (1.5 to 4.0 cm) long, sometimes up to 2¾″ (7 cm) long. The terminal spike is frequently club-shaped. The perigynium is usually 1⁄16″ to ⅛″ (2.0 to 2.5 mm) long, sometimes 1⁄16″ (1.5 mm) long. It is much more common. |
Habitat |
Moist. Sun or shade. Forested peatlands, mires, thickets, mixed, moderately moist forests; swales, and rock outcrops. |
Ecology |
Flowering |
May to June |
Maturing |
Early June to early August |
Pests and Diseases |
|
Use |
|
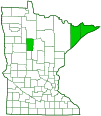
Distribution |
||
|
Sources |
|
| 6/18/2024 | ||
Nativity |
||
Native |
||
Occurrence |
||
|
||
Taxonomy |
|
Kingdom |
|
| Phylum |
Tracheophyta (Vascular Plants) |
Subdivision |
Spermatophytina (Seed Plants) |
Class |
Liliopsida (Monocots) |
Order |
Poales (Grasses, Sedges, Cattails, and Allies) |
Family |
Cyperaceae (sedges) |
Subfamily |
Cyperoideae |
Tribe |
Cariceae |
Genus |
Carex (true sedges) |
Subgenus |
Vignea |
Section |
Glareosae |
| Species | Carex brunnescens (brownish sedge) |
Subordinate Taxa |
|
|
|
Synonyms |
|
Carex alpicola Carex brunnescens ssp. alaskana Carex brunnescens ssp. pacifica Carex brunnescens ssp. vitilis Carex brunnescens var. brunnescens Carex brunnescens var. laetior Carex brunnescens var. silvatica Carex brunnescens var. vitilis Carex canescens ssp. vitilis Carex canescens var. alpicola Carex canescens var. persoonii Carex canescens var. vitilis Carex curta var. alpicola Carex gebhardii Carex gracilis Carex persoonii ssp. vitilis Carex persoonii var. laetior Carex vitilis Carex vitilis f. pallida Carex vitilis var. brunnea Carex vitilis var. sylvatica Vignea brunnescens ssp. alaskana Vignea brunnescens ssp. pacifica Vignea brunnescens ssp. vitilis |
|
Common Names |
|
brownish sedge |
|
Glossary
Achene
A dry, one-chambered, single-seeded seed capsule, formed from a single carpel, with the seed attached to the membranous outer layer (wall) only by the seed stalk; the wall, formed entirely from the wall of the superior ovary, does not split open at maturity, but relies on decay or predation to release the contents.
Beak
In plants: A comparatively short and stout, narrow or prolonged tip on a thickened organ, as on some fruits and seeds. In insects: The protruding, tubular mouthpart of a sucking insect.
Bract
Modified leaf at the base of a flower stalk, flower cluster, or inflorescence.
Culm
The hollow or pithy stem of a grass, sedge, or rush.
Ligule
In grasses and sedges, an outgrowth on the leaf at the junction of the blade and the sheath, usually membranous, sometimes no more than a fringe of hairs. In flowering plants, the ligule is the flat, strap-shaped, petal-like portion of the corolla of a ray floret.
Perigynium
In Carex and other closely related sedges, a sac-like or flask-shaped, highly modified bract that surrounds the pistillate flower and later encloses the achene. Plural: perigynia.
Raceme
An unbranched, elongated inflorescence with stalked flowers. The flowers mature from the bottom up.
Rhizome
A horizontal, usually underground stem. It serves as a reproductive structure, producing roots below and shoots above at the nodes.
Sheath
The lower part of the leaf that surrounds the stem.
Spike
The arrangement of an unbranched, elongated inflorescence with stalkless flowers that mature from the base toward the tip. In Cyperaceae, it also denotes a collection of one or a group of stalkless flowers, each subtended by scales, on a single inflorescence axis.
Visitor Photos |
||
Share your photo of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
||
|
||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
||
|
||
|
||

Slideshows |
|

Visitor Videos |
||
Share your video of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
Other Videos |
||
|

Visitor Sightings |
||
Report a sighting of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
|
MinnesotaSeasons.com Sightings |
||
|

|
Created: 6/19/2024 Last Updated: © MinnesotaSeasons.com. All rights reserved. |