twinflower
(Linnaea borealis ssp. americana)
Conservation • Wetland • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Use • Distribution • Taxonomy
Description |
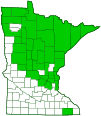
Twinflower is a perennial, ground-hugging, evergreen, dwarf shrub (subshrub). It occurs throughout Canada. In the United States it occurs in the east from Maine south to New York and west to Minnesota, and in the west from Washington east to Montana and south to northern California. In Minnesota it is very common in the northeast and north-central regions, uncommon in the metro and southeast regions, and absent from the south and southwest regions. There are a few occurrences in the north-western counties and only a single occurrence in Fillmore County along the South Branch Root River. Twinflower sometimes forms large colonies. It is found in deciduous, coniferous, and mixed forests and woodlands, thickets, cedar swamps, and bogs, in moist or moderately moist conditions. It grows under partial shade in peat, on rotting logs, and on mossy boulders. The stems are slender, 3′ to 6′ (1 to 2 m) long, and lie flat on the ground (prostrate). They are slightly woody, reddish-brown, and covered with short, fine hairs. Older stems are woody and 1⁄16″to ⅛″ (2 to 4 mm) in diameter. Every few inches a branch rises from a node. Branches can be 2″ to 6″ tall but are usually no more than 4″ in height. They are erect, slender, reddish-brown, leafy, and hairy. New roots are produced where a node touches the ground or other substrate. After many years the stem may separate there and a new plant is created. The leaves are opposite, evergreen, somewhat leathery, ⅜″ to 11⁄16″ (9 to 18 mm) long, and ¼″ to ⅝″ (7 to 15 mm) wide. They are on 1⁄16″ to 3⁄16″ (2 to 5 mm) long leaf stalks. The leaf blades are egg-shaped (widest below the middle), inversely egg-shaped (widest above the middle), or elliptical (widest at the middle), to almost circular. They are angled at the base and rounded at the tip. The upper surface is dark green and sparsely covered with fine hairs. The lower surface is pale green and hairless or almost hairless. The margins have 1 to 4 rounded teeth above the middle on each side. Smaller leaves are often untoothed. The inflorescence is a pair of flowers at the end of an erect, 1⅜″ to 3⅛″ (3.5 to 8 cm) long, inflorescence stalk (peduncle). Each flower droops at the end of a short, less than ⅜″ long, flower stalk (pedicel). The peduncle and pedicel are covered with gland-tipped hairs. There is a small modified leave (bract) at the base of each pedicel. Each flower is bell-shaped and 5⁄16″ to ½″ (8 to 12 mm) long. There are 5 outer floral leaves (sepals), 5 petals, 4 stamens, and 1 style. The ovary, at the base of each flower, has two pairs of modified leaves, an outer, large, shield-like pair, and an inner, minute pair. The ovary and outer bracts are covered with gland-tipped hairs. The sepals (together the calyx) are green, united at the base into a short tube then separated into 5, narrow, 1⁄16″to ⅛″ (2 to 3 mm) long lobes. The sepals are covered with gland-tipped hairs. They fall off when the plant is in fruit. The petals (together the corolla) are pink at the base, white at the tip. They are united at the base for more than half of their length into a funnel-shaped tube then separated into 5 pointed lobes. The inner surface of the corolla is densely covered with long hairs. The outer surface is hairless. The stamens are short and do not protrude from the corolla tube. The style has a slender white stalk and a cap-like stigma. It protrudes beyond the corolla tube. The fruit is a yellow, dry, globe-shaped, 1⁄16″ (2 mm) in diameter capsule with 1 seed. The fruit droops at the end of the pedicel and is enclosed by the persistent outer bracts. |
Height |
2″ to 4″ |
Flower Color |
Pink to white |
Similar Species |
|
Habitat |
Moist or moderately moist. Deciduous, coniferous, and mixed forests and woodlands, thickets, cedar swamps, and bogs. Partial shade. Peat, rotting logs, and mossy boulders. |
Ecology |
Flowering |
Early mid-June to early August |
Pests and Diseases |
|
Use |
|
Distribution |
||
|
Sources |
|
| 6/25/2024 | ||
Nativity |
||
Native |
||
Occurrence |
||
Very common |
||
Taxonomy |
|
Kingdom |
|
Subkingdom |
Pteridobiotina |
Phylum |
Tracheophyta (Vascular Plants) |
Class |
|
Order |
Dipsacales (honeysuckles, moschatels, and allies) |
Family |
Caprifoliaceae (honeysuckle) |
Subfamily |
Linnaeoideae (abelias, twinflower and allies) |
Genus |
Linnaea (twinflowers) |
Species |
Linnaea borealis (twinflower) |
There is no consensus as to the correct number and placement of the subordinate taxa of Linnaea borealis, including whether they are subspecies or varieties. The names Linnaea borealis ssp. americana, Linnaea borealis var. americana, Linnaea borealis ssp. borealis, Linnaea borealis var. borealis, Linnaea borealis ssp. longiflora, and Linnaea borealis var. longiflora, are all currently in use. According to GBIF and Catalog of Life, L. b. ssp. longiflora and L. b. var. longiflora are synonyms of L. b. var. americana. According to ITIS and World Flora Online, L. b. ssp. americana and L. b. var. americana are synonyms of L. b. var. longiflora. According to GRIN, L. b. var. americana is a synonym of L. b. var. longiflora. According to USDA PLANTS, L. b. ssp. americana, L. b. ssp. borealis, and L. b. ssp. longiflora are all distinct subspecies. According to Plants of the World Online, L. b. var. americana, L. b. var. borealis, and L. b. var. longiflora are all distinct varieties. Whetever the case, only one subspecies or variety occurs in Minnesota, and it is not ssp. borealis or var. borealis. |
|
Synonyms |
|
Linnaea americana Linnaea borealis var. americana Linnaea borealis ssp. longiflora |
|
Common Names |
|
American twinflower twinflower |
|
Glossary
Bract
Modified leaf at the base of a flower stalk, flower cluster, or inflorescence.
Calyx
The group of outer floral leaves (sepals) below the petals, occasionally forming a tube. Plural: calyces.
Corolla
A collective name for all of the petals of a flower.
Node
The smal l swelling of the stem from which one or more leaves, branches, or buds originate.
Pedicel
On plants: the stalk of a single flower in a cluster of flowers. On insects: the second segment of the antennae. On Hymenoptera and Araneae: the narrow stalk connecting the thorax to the abdomen: the preferred term is petiole.
Peduncle
In angiosperms, the stalk of a single flower or a flower cluster; in club mosses, the stalk of a strobilus or a group of strobili.
Prostrate
Laying flat on the ground.
Sepal
An outer floral leaf, usually green but sometimes colored, at the base of a flower.
Visitor Photos |
||
Share your photo of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
Luciearl |
||
 |
 |
|
This plant likes to grow in shady mossy areas. |
||
|
||
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
||
 |
|

Slideshows |
|

Visitor Videos |
||
Share your video of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
Other Videos |
||
|

Visitor Sightings |
||
Report a sighting of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
| Luciearl 6/24/2024 |
Location: Fairview Twp |
 |
| Luciearl 10/20/2022 |
Location: Fairview Twp, Cass County This plant likes to grow in shady mossy areas. |
 |
| Luciearl 9/30/2020 |
Location: Cass County |
 |
MinnesotaSeasons.com Sightings |
||
|

Created: 11/2/2020 Last Updated: © MinnesotaSeasons.com. All rights reserved. |