goat’s rue
(Tephrosia virginiana)
Conservation • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Use • Distribution • Taxonomy
Conservation Status |
|
|||||||
| IUCN Red List | not listed |
|||||||
| NatureServe | N5 - Secure S3 - Vulnerable |
|||||||
| Minnesota | Special Concern |
|||||||
Description |
||
Goat’s rue is a showy summer wildflower. It occurs in the United States east of the Great Plains. It is rare in Minnesota, where it reaches the northwest extent of its range. It is restricted to a handful of counties in the extreme southeast, and is listed as a special concern species in the state. It is found in prairies, savannas, open woodlands, and roadsides. It grows under full or partial sun, in dry to moderately moist conditions, in sandy soil. Though infrequent, where it occurs it is often in large colonies. Goat’s rue is an erect, perennial forb that rises on one to several stems from a thick, knobby base (caudex) and long woody roots. It can be 8 ″ to 27½″ (20 to 70 cm) tall but is usually no more than 20 ″ (50 cm) in height. The plant is easy to identify when flowers or fruit are present, difficult to identify when they are not. The stems are erect or curve up from the base (ascending) and are often clustered. They are usually unbranched but may have one or more weak branches. They are usually densely covered, sometimes moderately covered, with fine, appressed and spreading hairs. The leaves are alternate, pinnately compound, and 2″ to 6″ long. There are usually 13 to 25 leaflets but there may be as few as 9 or as many as 31. At the base of each leaflet there is a pair of small, leaf-like appendages (stipules). Stipules on lower leaves are narrowly elliptic or lance-shaped to linear and ¼″ to 7⁄16″ (7 to 11 mm) in length. Those on upper leaves are often hairlike. They drop off early. The central axis (rachis) of the leaf is 1½″ to 4¾″ (4 to 12 cm) long. The leaflets are narrowly elliptic to inversely lance-shaped, narrowly oblong, or linear, ½″ to 1 3⁄16″ (12 to 30 mm) long, and 1⁄16″ to ⅜″ (2 to 10 mm) wide. They are angled to rounded at the base and taper to a blunt or sharp point at the tip. The midvein of the leaflet usually continues to a needle-like point at the tip. The terminal leaflet is sometimes rounded or notched at the tip. The upper surface is medium green or grayish-green, and may be hairless or moderately to densely covered with short, fine, curved hairs. The lower surface is densely covered with appressed hairs. The lateral veins are noticeable on the underside. The margins are untoothed and usually have a fringe of ascending hairs. The inflorescence is a short, dense, unbranched cluster (raceme) of 12 to 40 flowers at the end of the stem. The raceme is 1½″ to 3″ (4 to 8 cm) long and is on a ⅜″ to 1¼″ (1 to 3 cm) long stalk. There are sometimes smaller racemes at the tips of the branches. Each flower is on a ⅛″ to ¾″ (4 to 20 mm) long, densely hairy stalk (pedicel). At the base of each pedicel there is a single modified leaf (bract). The bract is 3⁄16″ to ½″ (6 to 12 mm) long, sometimes longer. It withers early but usually remains on the plant throughout the flowering and fruiting time. Each flower is about ¾″ long and wide. There are 5 outer floral leaves (sepals), 5 petals, 10 stamens, and 1 style. The sepals are light green, densely hairy, and fused for most of their length into a bell-shaped, 1⁄16″ to 3 ⁄16″ (2 to 5 mm) long tube (calyx), then separated into 2 lips, the upper lobe with 2 lobes, the lower lip with 3 lobes. The petals are organized into a typical pea-like arrangement, with an upper banner, a pair of lateral wing petals, and a pair of lower keel petals. The banner is ⅝″ to ¾″ (15 to 19 mm) long, ½″ to 11⁄16″ (12 to 18 mm) wide, broadly kidney-shaped to almost circular, and broadly pointed, rounded, or slightly notched at the tip. It is abruptly bent upward near the base and is keeled for its entire length. The outer surface is hairy. It is green at first, then turns yellow or cream-colored at maturity. The inner surface is white to cream-colored with a yellow patch near the base surrounded by a pink-tinged area. The wings are ½″ to ¾″ (12 to 20 mm) long, 3⁄16″ to ¼″ (5 to 7 mm) wide, rosy pink, oblong egg-shaped, and rounded at the tip. They are angled over and completely cover the keel. The keel is ½″ to ⅝″ (12 to 15 mm) long and 3⁄16″ to ¼″ (5 to 7 mm) wide, boat-shaped, and curved upward at the tip. It is light pink or light yellow with a pink tinge or pink lines. Nine of the stamens have their stalks (filaments) fused together, one is free to below the middle. The anthers are small and yellow. The style is 5⁄16″ to 7⁄16″ (8 to 11 mm) long and has a minute stigma at the tip. The fruit is a 1¼″ to 2″ (3 to 5 cm) long, ⅛″ to ¼″ (3 to 6 mm) wide pod with 6 to 11 seeds. It is narrowly oblong, straight or slightly curved, and has a slender, often curved beak at the tip. The outer surface is sparsely to densely hairy, light green at first, becoming papery and straw-colored to brown at maturity. The seeds are kidney-shaped and ⅛″ to 3⁄16″ long. |
||
Height |
||
8 ″ to 27½″ (20 to 70 cm) |
||
Flower Color |
||
Yellow or cream colored and rosy pink |
||
Similar Species |
||
Leadplant (Amorpha canescens), with its grayish-green leaflets, looks similar when flowers and fruit are not present. However, its leaflets are rounded to slightly heart-shaped at the base. |
||
Habitat |
||
Dry to moderately moist. Prairies, savannas, open woodlands, and roadsides. Full or partial sun. Sandy soil. |
||
Ecology |
||
Flowering |
||
Mid-June to late July |
||
Pests and Diseases |
||
|
||
Use |
||
Toxicity |
||
All parts of the plant are poisonous to both livestock and people. |
||
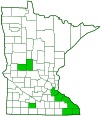
Distribution |
||||
|
Sources |
|||
| 12/16/2021 | ||||
Nativity |
||||
Native |
||||
Occurrence |
||||
Rare in Minnesota |
||||
Taxonomy |
|||
| Kingdom | Plantae (Plants) | ||
| Subkingdom | Pteridobiotina | ||
| Phylum | Tracheophyta (Vascular Plants) | ||
| Class | Magnoliopsida (Dicots) | ||
Order |
Fabales (Legumes, Milkworts, and Allies) | ||
Family |
Fabaceae (Legumes) | ||
Subfamily |
Faboideae | ||
Tribe |
Millettieae | ||
Genus |
Tephrosia (hoarypeas) | ||
Subordinate Taxa |
|||
|
|||
Synonyms |
|||
Cracca latidens Cracca virginiana Tephrosia latidens Tephrosia virginiana var. glabra Tephrosia virginiana var. holosericea |
|||
Common Names |
|||
cagut goat’s rue goat’s-rue rabbit-pea Virginia tephrosia |
|||
Glossary
Ascending
Growing upward at an angle or curving upward from the base.
Beak
In plants: A comparatively short and stout, narrow or prolonged tip on a thickened organ, as on some fruits and seeds. In insects: The protruding, tubular mouthpart of a sucking insect.
Bract
Modified leaf at the base of a flower stalk, flower cluster, or inflorescence.
Calyx
The group of outer floral leaves (sepals) below the petals, occasionally forming a tube. Plural: calyces.
Caudex
A short, thickened, woody, persistent enlargement of the stem, at or below ground level, used for water storage.
Filament
On plants: The thread-like stalk of a stamen which supports the anther. On Lepidoptera: One of a pair of long, thin, fleshy extensions extending from the thorax, and sometimes also from the abdomen, of a caterpillar.
Keeled
Folded, as in a grass blade, or with a raised ridge, as in a grass sheath; like the keel of a boat.
Linear
Long, straight, and narrow, with more or less parallel sides, like a blade of grass.
Pedicel
On plants: the stalk of a single flower in a cluster of flowers. On insects: the second segment of the antennae. On Hymenoptera and Araneae: the narrow stalk connecting the thorax to the abdomen: the preferred term is petiole.
Pinnate
On a compound leaf, having the leaflets arranged on opposite sides of a common stalk. On a bryophyte, having branches evenly arranged on opposite sides of a stem.
Raceme
An unbranched, elongated inflorescence with stalked flowers. The flowers mature from the bottom up.
Rachis
The main axis of a compound leaf, appearing as an extension of the leaf stalk; the main axis of an inflorescence.
Sepal
An outer floral leaf, usually green but sometimes colored, at the base of a flower.
Stigma
In plants, the portion of the female part of the flower that is receptive to pollen. In Lepidoptera, an area of specialized scent scales on the forewing of some skippers, hairstreaks, and moths. In other insects, a thickened, dark, or opaque cell on the leading edge of the wing.
Stipule
A small, leaf-like, scale-like, glandular, or rarely spiny appendage found at the base of a leaf stalk, usually occurring in pairs and usually dropping soon.
Visitor Photos |
|||||
Share your photo of this plant. |
|||||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Attach one or more photos and, if you like, a caption. |
|||||
Nancy Falkum |
|||||
Goat’s-rue Tephrosia virginiana At TNC KWD Cox Unit |
|||||
 |
|||||
Tephrosia virginiana Goat’s-rue at TNC Cox Unit |
|||||
 |
|||||
Goat’s Rue |
|||||
 |
 |
||||
Goat’s Rue with Blanding’s turtle |
|||||
 |
|||||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
|||||
|
|||||

Slideshows |
||

Visitor Videos |
|||
Share your video of this plant. |
|||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Attach a video, a YouTube link, or a cloud storage link. |
|||
Other Videos |
|||
| Goat's Rue - Tephrosia virginiana Eric Hunt |
|||
About
Sep 5, 2020 Video taken at the Camp Robinson Special Use Area Wildlife Management Area, Faulkner County, Arkansas |
|||
| Tephrosia virginiana Common Name(s): Goat's Rue Virginia Goat's Rue ArkWildman survival |
|||
About
Jun 5, 2021 The seeds are toxic[222]. The plant contains rotenonoids and has been used traditionally as a fish poison - rotenoids kill or stun the fish making them easy to catch, but the fish remain perfectly edible for mammals. Rotenonoids are classified by the World Health Organization as moderately hazardous. They are mildly toxic to humans and other mammals, but extremely toxic to many insects (hence their use as an insecticide) and aquatic life, including fish. This higher toxicity in fish and insects is because the lipophilic rotenonoid is easily taken up through the gills or trachea, but not as easily through the skin or the gastrointestinal tract. The lowest lethal dose for a child is 143 mg/kg, but human deaths from rotenone poisoning are rare because its irritating action causes vomiting. Deliberate ingestion of rotenone, however, can be fatal. |
|||
| Goat's Rue Kansas Land Trust |
|||
About
Jun 18, 2020 Kelly Kindscher talks about Goat's Rue on the Akin Prairie. |
|||

Visitor Sightings |
|||||
Report a sighting of this plant. |
|||||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Be sure to include a location. |
|||||
| Nancy Falkum 6/26/2022 |
Location: Weaver Dunes Preserve, Cox Unit Goat’s-rue Tephrosia virginiana At TNC KWD Cox Unit |
||||
| Nancy Falkum 6/16/2022 |
Location: Weaver Dunes Preserve, Cox Unit Tephrosia virginiana Goat’s-rue at TNC Cox Unit |
||||
| Nancy Falkum 6/17/2021 |
Location: Kellogg Weaver Dunes SNA, Weaver Dunes Unit Goat’s Rue |
||||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Sightings |
|||||

Created: 12/16/2021
Last Updated: