water speedwell
(Veronica catenata)
Conservation • Wetland • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Use • Distribution • Taxonomy
Description |
||
Water speedwell is a large semi-aquatic plant. It occurs across the United States and southern Canada. It is common in Minnesota. It grows in full sun, in muddy or sandy and gravelly soil, in springs, slow streams, edges of ponds, and ditches. Due to the uncertain taxonomy of this species, its distribution is uncertain. Some reputable sources believe this is the European species blue water speedwell (Veronica anagallis-aquatica). They contend that it is not native but was introduced into North America and is now widely naturalized. Other equally reputable sources insist that this is a separate species native to North America. They contend that the two species are easily separable by visible characteristics. Most sources list only one of the two species in North America. A few show both species occurring in the United States. In either case, there is intergradation of the characteristics and separation of the two species in the field is not as clear as the plant identification dichotomous keys would make it seem. Making matters worse, the two plants readily hybridize. Water speedwell is an erect, perennial forb that rises on multiple stems from a thin, underground, horizontal stem (rhizome) and fibrous roots. It can be 8″ to 40″ tall but is usually no more than 24″ in height. It is often emergent, with the base of the plant under water. Sometimes it is completely submerged. The stems are usually erect or curve up strongly from the base (ascending). In areas with flooding they may be nearly horizontal (spreading). They are branched and usually completely hairless. Sometimes they are sparsely to moderately covered with minute, gland-tipped hairs just in the inflorescence. Roots develop at the lowest nodes. The leaves are opposite, ¾″ to 3⅛″ long, ¼″ to 1½″ wide, mostly lance-shaped (widest below the middle), sometimes inversely lance-shaped (widest above the middle) or oblong (widest and with straight sides along the middle). Most are 3 to 5 times as long as wide, though some may be up to 8 times as long as wide, especially just below the inflorescence. Most are stalkless but the lower leaves sometimes have short leaf stalks. The leaf blades are heart-shaped at the base and are mostly sharply pointed, sometimes bluntly pointed at the tip. The stalkless leaves more or less wrap partially around (clasp) the stem at the base. The upper surface is hairless and minutely pitted, though this requires a hand lens to see. The lower surface is mostly hairless but may have inconspicuous gland-tipped hairs near the base of the midrib. The margins may be untoothed or have minute, widely-spaced teeth, especially near the tip. The inflorescence is a solitary unbranched cluster (raceme) of 15 to 25 flowers rising from each of the upper leaf axils. The raceme is up to about 2¾″ (7 cm) long and is on a hairless stalk (peduncle) that is up to 1 9 ⁄16″ (4 cm) long. Each flower is on a spreading to ascending, ⅛″ to 3 ⁄16″ (2.5 to 5 mm) long stalk (pedicel). When in fruit, the pedicel lengthens to ¼″ (7 mm) and spreads at a right angle to the axis of the raceme or occasionally slightly curves upward. At the base of each pedicel there is a single, small, modified leaf (bract). The bract is narrow, 1 ⁄16″ to ⅛″ (1.5 to 4 mm) long, 1 ⁄16″ wide, and straight-sided (linear) or lance-shaped. The flowers are ⅛″ to ¼″ (3 to 6 mm) in diameter. There are 4 outer floral leaves (sepals), 4 petals, 2 stamens, and 1 style. The sepals are green and ⅛″ (3.0 to 3.5 mm) long. They are hairless or may have minute, gland-tipped hairs toward the base. They are fused at the base into a short, 1 ⁄32″ (1 mm) long calyx tube, then separated into 4 broadly lance-shaped to egg-shaped lobes. The petals (corolla) are fused at the base into a short tube then separated into 4 lobes that are much longer than the tube. The throat is green inside and there is a narrow white ring where the lobes separate. The corolla lobes are broadly egg-shaped, ⅛″ (3 mm) long and wide, and slightly curved upward. The upper and lateral lobes are equal in size, the lower lobe is smaller. All of the lobes are white to pink or pale bluish with darker purple veins. On the upper lobe and the upper half of the lateral lobes the veins are even darker and widen at the base. The stamens are ⅛″ (2.5 to 3.0 mm) long and project well beyond the petals. The stalks of the stamens (filaments) are white, becoming tinged with purple toward the tip. The style is ⅛″ (3 mm) long and also projects well beyond the petals. It is also white at the base and purplish tinged toward the tip. The fruit is a slightly flattened, ⅛″ (3 to 4 mm) long and wide capsule with numerous tiny seeds. The capsule is broadly triangular or slightly heart-shaped with just a shallow notch at the tip. The surfaces are hairless. The margin may be hairless or have a few gland-tipped hairs. |
||
Height |
||
8″ to 40″ |
||
Flower Color |
||
White to pink or pale bluish with purple streaks |
||
Similar Species |
||
Habitat |
||
Wet. Springs, slow streams, edges of ponds, and ditches. Full to partial sun. Muddy or sandy and gravelly soil. |
||
Ecology |
||
Flowering |
||
May to September |
||
Pests and Diseases |
||
|
||
Use |
||
|
||
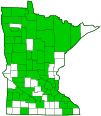
Distribution |
||||
|
Sources |
|||
| 4/1/2023 | ||||
Nativity |
||||
Native |
||||
Occurrence |
||||
Common and widespread |
||||
Taxonomy |
|||
| Kingdom | Plantae (Plants) | ||
| Subkingdom | Pteridobiotina | ||
| Phylum | Tracheophyta (Vascular Plants) | ||
| Class | Magnoliopsida (Dicots) | ||
Order |
Lamiales (Mints, Plantains, Olives, and Allies) | ||
Family |
Plantaginaceae (plantain) | ||
| Tribe | Veroniceae | ||
| Genus | Veronica (speedwells) | ||
| Subgenus | Beccabunga | ||
Some sources, including BONAP and USDA PLANTS, consider this plant the same as the European species blue water speedwell (Veronica anagallis-aquatica). Most sources list only one of the two species in North America. At least three sources, including Gleason & Cronquist, GBIF, and iNaturalist, show both species occurring in the United States. In plant identification dichotomous keys the two species are easily separable by visible characteristics. In the field, however, there is intergradation of the characteristics and separation of the two species is not as clear. Making matters worse, the two plants readily hybridize, and the offspring exhibit intermediate characteristics. |
|||
Subordinate Taxa |
|||
Some authors recognize the variety var. glandulosa. These plants have gland-tipped hairs on the stem, whereas the nominate variety (var. catenata) stems are hairless. The fruit is sometimes slightly narrower. Most authors consider the differences too slight to warrant separation, and recognize no varieties. |
|||
Synonyms |
|||
Veronica catenata var. glandulosa Veronica comosa var. glaberrima Veronica comosa var. glandulosa Veronica connata Veronica connata ssp. glaberrima Veronica connata var. glaberrima Veronica connata var. typica |
|||
Common Names |
|||
chain speedwell Pennell’s speedwell pink water-speedwell sessile water-speedwell water speedwell |
|||
Glossary
Ascending
Growing upward at an angle or curving upward from the base.
Axil
The upper angle where a branch, stem, leaf stalk, or vein diverges.
Bract
Modified leaf at the base of a flower stalk, flower cluster, or inflorescence.
Clasping
Describing a leaf that wholly or partly surrounds the stem but does not fuse at the base.
Filament
On plants: The thread-like stalk of a stamen which supports the anther. On Lepidoptera: One of a pair of long, thin, fleshy extensions extending from the thorax, and sometimes also from the abdomen, of a caterpillar.
Glandular hairs
Hairs spread over aerial vegetation that secrete essential oils. The oils act to protect against herbivores and pathogens or, when on a flower part, attract pollinators. The hairs have a sticky or oily feel.
Linear
Long, straight, and narrow, with more or less parallel sides, like a blade of grass.
Node
The small swelling of the stem from which one or more leaves, branches, or buds originate.
Pedicel
On plants: the stalk of a single flower in a cluster of flowers. On insects: the second segment of the antennae. On Hymenoptera and Araneae: the narrow stalk connecting the thorax to the abdomen: the preferred term is petiole.
Peduncle
In angiosperms, the stalk of a single flower or a flower cluster; in club mosses, the stalk of a strobilus or a group of strobili.
Raceme
An unbranched, elongated inflorescence with stalked flowers. The flowers mature from the bottom up.
Rhizome
A horizontal, usually underground stem. It serves as a reproductive structure, producing roots below and shoots above at the nodes.
Sepal
An outer floral leaf, usually green but sometimes colored, at the base of a flower.
Spreading
Extending nearly horizontal.
Visitor Photos |
|||||
Share your photo of this plant. |
|||||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Attach one or more photos and, if you like, a caption. |
|||||
|
|||||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
|||||
Plant |
|||||
 |
 |
||||
Inflorescence |
|||||
 |
 |
||||
 |
|||||
Flowers |
|||||
 |
 |
||||
Leaves |
|||||
 |
 |
||||

Slideshows |
||

Visitor Videos |
|||
Share your video of this plant. |
|||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Attach a video, a YouTube link, or a cloud storage link. |
|||
Other Videos |
|||
| Veronica anagallis aquatica is a species of flowering plant in the family Plantaginaceae The Living World |
|||
About
May 21, 2019 I go through the forests, mountains, hills, fields, and waters to understand the living world and to create a living mind. Veronica anagallis-aquatica is a species of flowering plant in the family Plantaginaceae known by the common names water speedwell, blue water-speedwell, brook pimpernel, and sessile water-speedwell, Veronica catenata. |
|||

Visitor Sightings |
|||||
Report a sighting of this plant. |
|||||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Be sure to include a location. |
|||||
|
|||||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Sightings |
|||||

Created: 12/20/2019
Last Updated: