red running crab spider
(Philodromus rufus vibrans)
Conservation • Description • Habitat • Biology • Distribution • Taxonomy
Conservation Status |
|
|||||||
| IUCN Red List | not listed |
|||||||
| NatureServe | NNR - Unranked |
|||||||
| Minnesota | not listed |
|||||||
Description |
||
White-striped running crab spider (Philodromus rufus) is relatively small, hairy, and drably colored. It is widely distributed across Europe, the United States, and Canada. Red running crab spider (Philodromus rufus vibrans) is the smallest of three North American subspecies. It is the only subspecies that has been recorded in Minnesota. It is found on coniferous and deciduous trees and shrubs, and often in or on buildings. Females are 3 ⁄16″ (3.75 mm) long and have a legspan of ⅝″ to ¾″. Males are slightly smaller, ⅛″ (3.40 mm) in length. The covering (carapace) of the front part of the body (cephalothorax) is about as long as wide, is somewhat flattened, and has smoothly convex lateral margins. It is yellowish-brown and is covered with shiny hairs. The pale upper middle (median) area is yellowish-orange and speckled with tiny brown spots. The lateral areas are yellowish-brown with a dense covering of fine brown spots and narrow black streaks. The head is slightly angled upward. The eight eyes are black and are arranged in two rows of four each. The four eyes in the front row are all equal in size. In the back row, the middle (median) eyes are closer to the lateral eyes than they are to each other. The abdomen is flattened, is somewhat angular at the sides, and covered with hairs. The hairs on the carapace and abdomen are soft, not erect. On the female, the pale median area is yellowish with dark brown markings. The lateral areas are brownish. There is a brown median stripe on the front (anterior) half, and a pair of brown oblique stripes on the rear (posterior) half. The male is much darker and shows less patterning. The legs are long, slender, yellowish, and speckled with fine brown to black spots. They are optimized for lateral movement. The second pair is slightly longer than the others, which are about equal in length and thickness. The first four segments of each leg are armed with long, stiff, spine-like hairs. The last leg segment (tarsus) has a two claws, a dense, brush-like tuft of microscopic hairs below (scopula), and a dense, brush-like tuft of microscopic hairs at the end (claw tuft). The claws, scopulae, and claw tufts are not visible to the naked eye. |
||
Size |
||
Female Body Length: 3 ⁄16″ (3.75 mm) Male Body Length: ⅛″ (3.40 mm) Legspan: ⅝″ to ¾″ |
||
Web |
||
|
||
Similar Species |
||
Habitat |
||
Coniferous and deciduous trees and shrubs; in or on buildings |
||
Biology |
||
Season |
||
|
||
Behavior |
||
This spider does not produce a web to catch prey. It hunts actively, running after prey, and passively, lying in wait and ambushing prey. It is very fast and difficult to see. During courtship, the male rapidly vibrates its front legs. |
||
Life Cycle |
||
The female spins a nursery web for its eggs in the summer. It guards the web until the young spiderlings have dispersed. The last stage (instar) spiderling overwinters. |
||
Food |
||
|
||
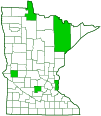
Distribution |
||||
|
Sources |
|||
| 5/26/2022 | ||||
Occurrence |
||||
Fairly common |
||||
Taxonomy |
|||
| Class | Arachnida (arachnids) | ||
Order |
Araneae (spiders) | ||
Suborder |
Araneomorphae (typical spiders) | ||
| Infraorder | Entelegynae (entelegyne spiders) | ||
Superfamily |
Thomisoidea (crab and running crab spiders) | ||
Family |
Philodromidae (running crab spiders) | ||
Genus |
Philodromus | ||
Species |
Philodromus rufus (white-striped running crab spider) | ||
Synonyms |
|||
Philodromus pictus Philodromus vibrans |
|||
Common Names |
|||
red running crab spider |
|||
Glossary
Carapace
The hard, upper (dorsal), shell-like covering (exoskeleton) of the body or at least the thorax of many arthropods and of turtles and tortoises. On crustaceans, it covers the cephalothorax. On spiders, the top of the cephalothorax made from a series of fused sclerites.
Cephalothorax
The front part of a spider’s body, composed of the head region and the thoracic area fused together. Eyes, legs, and antennae are attached to this part.
Instar
The developmental stage of arthropods between each molt; in insects, the developmental stage of the larvae or nymph.
Tarsus
On insects, the last two to five subdivisions of the leg, attached to the tibia; the foot. On spiders, the last segment of the leg. Plural: tarsi.
Visitor Photos |
|||||
Share your photo of this arachnid. |
|||||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Attach one or more photos and, if you like, a caption. |
|||||
Alfredo Colon |
|||||
 |
 |
||||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
|||||
|
|||||

Visitor Videos |
|||
Share your video of this insect. |
|||
| This button not working for you? Simply email us at info@MinnesotaSeasons.com. Attach a video, a YouTube link, or a cloud storage link. |
|||
Other Videos |
|||

Created 12/7/2018
Last Updated: