American dog violet
(Viola labradorica)
Conservation • Wetland • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Use • Distribution • Taxonomy
Description |
American dog violet is a ½″ to 8″ tall, erect to drooping, perennial forb that rises on several clustered stems from an oblique, occasionally branched rhizome. It forms clumps. The stems are erect to drooping, leafy, and usually hairy. Leaves and flowers appear on the same stem. Basal leaves are large and on long stalks. They are thin, pale green, hairless, and kidney-shaped to roundish. They are rounded or blunt at the tip and heart-shaped at the base. The basal lobes are widely open, not overlapping. The margins have rounded teeth. Stem leaves are similar, smaller, alternate, round, ⅝″ to 1½″ wide, broadly-angled at the tip, and heart-shaped at the base. The inflorescence is numerous single flowers on slender, 2″ to 3″ long stalks rising from the leaf axils. The long-stalked flowers are held above the leaves. There are small, broadly lance-shaped, stipules at the base of the flower stalks. The stipules are bristly for more than half of their length. The flowers are ½″ to ¾″ wide. There are 5 petals in an arrangement typical of violets—two upper, two lateral, and a broad lower lip. The petals are light blue to pale violet, rarely white. The lateral and lower petals are pale or whitish with dark veins near the center. The lower petal has a ⅛″ to 3 ⁄16″ long spur at the base that curls upward behind the flower. The lateral petals have tufts of white hair near the center (bearded). The plant produces flowers when it is only ½″ in height. The fruit is an elliptical, ⅛″ to 3 ⁄16″ long capsule with light brown seeds. When the plant is in fruit the stipules are dry and translucent. |
Height |
½″ to 8″ |
Flower Color |
Light blue to pale violet |
Similar Species |
Long-spurred violet (Viola rostrata) has a longer spur, ¼″ to ½″ long. The lateral petals are not bearded. Great-spurred violet (Viola selkirkii) leaves and flowers rise from the ground on separate stalks. The basal lobes of the leaves are narrowly open, sometimes overlapping. The spur is rounded, blunt and tends to be larger, ⅛″ to ¼″ long. The lateral petals are not bearded. |
Habitat |
Dry to moderate moisture. Woods, meadows. Full sun to shade. |
Ecology |
Flowering |
June to August |
Pests and Diseases |
|
Use |
|
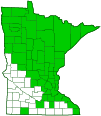
Distribution |
||
|
Sources |
|
| 5/15/2024 | ||
Nativity |
||
Native |
||
Occurrence |
||
Common |
||
Taxonomy |
|
Kingdom |
|
Subkingdom |
Pteridobiotina |
Phylum |
Tracheophyta (Vascular Plants) |
Class |
|
Order |
Malpighiales (Nances, Willows, and Allies) |
Family |
Violaceae (violet) |
Subfamily |
Violoideae |
Tribe |
Violeae |
Genus |
Viola (violets) |
Subgenus |
Viola (pansies and violets) |
Section |
Viola |
Subsection |
Rostratae |
This plant was formerly called American dog violet (Viola conspersa). It was described and published in 1823. A similar species, Alpine violet (Viola labradorica) had already been described and published in 1818. Over time, botanists came to the understanding that both descriptions were of the same species. The consensus emerged around 2009 and 2010. The name Viola labradorica was published earlier and therefore had priority. Online databases began making the change around 2009 and 2010. |
|
Subordinate Taxa |
|
|
|
Synonyms |
|
Viola adunca var. minor Viola conspersa |
|
Common Names |
|
alpine violet American dog violet dog violet early blue violet Labrador violet |
|
While its original common name was Labrador violet, alpine violet was more frequently used. Now, Labrador violet, alpine violet, American dog violet, and dog violet are all commonly used for this species. |
|
Glossary
Axil
The upper angle where the leaf stalk meets the stem.
Bearded
Bearing one or more tufts of hairs.
Rhizome
A horizontal, usually underground stem. It serves as a reproductive structure, producing roots below and shoots above at the nodes.
Stipule
A small, leaf-like appendage at the base of a leaf stalk or flower stalk.
Visitor Photos |
||
Share your photo of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
Luciearl |
||
 |
|
|
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
||
 |
 |
|
Clump |
||
 |
 |
|
Plant |
||
 |
||
Plant |
||
 |
 |
|
Flower |
||

Visitor Videos |
||
Share your video of this plant. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
Other Videos |
||
Viola labradorica |
About
Published on Mar 30, 2014 No description available. |

|
Created: Last Updated: © MinnesotaSeasons.com. All rights reserved. |