Frison’s soldier beetle
(Trypherus frisoni)
Conservation • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Distribution • Taxonomy
|
|
||||||||||||||
Description |
Frison’s soldier beetle is a medium-sized, soft-bodied, soldier beetle. It occurs in North America in the Midwest, from Ontario and Ohio in the east to Minnesota and Arkansas in the west. It is considered “not uncommon,” meaning that it occurs too frequently to be considered uncommon, bot not frequently enough to be considered common. Adults are ¼″ to ⅜″ long. The body is elongated, slender, and somewhat flattened, and has nearly parallel sides. The head is much wider than the exoskeletal plate covering the thorax (pronotum). It is visible from above, not completely concealed by the pronotum. It is black above, yellow in front around the bases of the antennae. The mouth parts (mandibles) are yellowish and are directed forward. The antennae have eleven segments. They are long, thread-like, and dark brown. On the female, the tip of the abdomen has three lobes. The pronotum is black with yellow margins. It is slightly wider than long and almost rectangular, with parallel sides, arced front margin, and wavy rear margin. It is flat above and has a broad, shallow, horse-shoe shaped depression near the middle of the base. The wing covers (elytra) are leathery, flexible, and black, with bright, orangish-yellow tips. They are short, about twice as long as the pronotum, and cover less than half of the abdomen. The hind wings are black and long, but do not completely cover the abdomen. The legs are long, slender, and mostly brownish-yellow. On the middle leg, the outer half of the third segment (femur) is black. On the hind leg, the tip of the femur and the entire fourth segment (tibia) are black. The end part of each leg (tarsus), corresponding to the foot, has 5 segments. The fourth segment has a lobe on the underside. On the middle and hind legs, the tarsi are black. |
Size |
Total length: ¼″ to ⅜″ |
Similar Species |
Habitat |
Prairies |
Ecology |
Season |
Mid-June to late July |
Behavior |
|
Life Cycle |
|
Larva Food |
|
Adult Food |
|
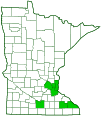
Distribution |
||
|
Sources |
|
| 7/4/2025 | ||
Occurrence |
||
|
||
Taxonomy |
|
Order |
Coleoptera (Beetles) |
Suborder |
Polyphaga (Water, Rove, Scarab, Long-horned, Leaf, and Snout Beetles) |
Infraorder |
Elateriformia |
Superfamily |
Elateroidea (click, firefly and soldier beetles) |
Family |
Cantharidae (soldier beetles) |
Subfamily |
Chauliognathinae |
Tribe |
Ichthyurini (shortwing soldierbeetles) |
Genus |
Trypherus |
Subordinate Taxa |
|
|
|
Synonyms |
|
|
|
Common Names |
|
Frison’s soldier beetle |
|
Glossary
Elytra
The hardened or leathery forewings of beetles used to protect the fragile hindwings, which are used for flying. Singular: elytron.
Femur
On insects and arachnids, the third, largest, most robust segment of the leg, coming immediately before the tibia. On humans, the thigh bone.
Pronotum
The exoskeletal plate on the upper side of the first segment of the thorax of an insect.
Scutellum
The exoskeletal plate covering the rearward (posterior) part of the middle segment of the thorax in some insects. In Coleoptera, Hemiptera, and Homoptera, the dorsal, often triangular plate behind the pronotum and between the bases of the front wings. In Diptera, the exoskeletal plate between the abdomen and the thorax.
Tarsus
On insects, the last two to five subdivisions of the leg, attached to the tibia; the foot. On spiders, the last segment of the leg. Plural: tarsi.
Tibia
The fourth segment of an insect leg, after the femur and before the tarsus (foot). The fifth segment of a spider leg or palp. Plural: tibiae.
Visitor Photos |
||
Share your photo of this insect. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
Alfredo Colon |
||
 |
||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
||
|
||
|
||

Slideshows |
|

Visitor Videos |
||
Share your video of this insect. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
Other Videos |
||
|

Created: 4/10/2019 Last Updated: © MinnesotaSeasons.com. All rights reserved. |