Dogwood agrilus
(Agrilus cephalicus)
Conservation • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Distribution • Taxonomy
|
|
||||||||||||||
Description |
Agrilus is one of the largest genera of animals in the world. There are about 2,900 species worldwide, most of which occur in the Asia Pacific region. There are 194 species in North America north of Mexico. Many are very similar in appearance and difficult if not impossible to distinguish by appearance alone. However, they are host species specialists. They can be identified by the plant on which the larvae and adults feed. Dogwood agrilus is a small, ¼″ (5.8 mm) long, 1 ⁄16″ (1.5 mm) wide, metallic wood-boring beetle. It is widely distributed but not common. The body is hard, narrow, elongated, parallel-sided, and moderately flattened above (dorsally). It varies from dark coppery brown to nearly black and has a metallic copper sheen. The upper plate covering the prothorax (pronotum) is wider than long and broadly rounded at the sides. It is slightly narrower than the base of the hardened wing covers (elytra). The elytra are slightly narrowed before the middle and tapered beyond the middle toward the tips. The tips are separated, broadly rounded, and finely toothed. Toward the tip the inner margins are slightly elevated. The antennae are short, extending only to about the middle of the pronotum. They are sawtoothed from the fourth segment to the tip. The larvae are known as flat-headed wood borers. They are elongated, narrow, slightly flattened, and whitish. The first segment of the thorax is widened and has a horny, plate-like surface with a line down the middle. This widened segment is the source of the common name of wood-boring larvae, flat-head. It has no legs but has a pair of forcep-like spines at the rear end of the abdomen. |
Size |
Total length: ¼″ |
Similar Species |
Many similar species but none hosted on dogwood. |
Habitat |
|
Ecology |
Season |
One generation: May to July |
Behavior |
On small stems the bark bulges over the larvae’s excavated gallery as it heals, betraying the presence of the wood-borer. When adults emerge they leave through a small D-shaped hole they chew in the bark. Adults are active on sunny days. They run rapidly to evade predators and collectors. If necessary, they will take flight. |
Life Cycle |
The female deposits eggs in crevices in the bark on a stem of the host. When the eggs hatch, the larvae bore through the bark, phloem, and cambium, to the surface of the sapwood. They excavate meandering galleries which are tightly filled with frass behind them. They pupate within the wood. Adults emerge from May to July. |
Larva Food |
Dogwood (Cornus spp.) phloem and cambium. The dogwood agrilus, as the name implies, attacks only dogwoods (Cornus spp.). It attacks trees or shrubs that have been injured or have been weakened by recent transplantation, insect infestation, or disease. They hasten the death of the host and are partially responsible for the decline of dogwoods in the southern states. |
Adult Food |
Dogwood (Cornus spp.) leaves |
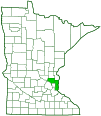
Distribution |
||
|
Sources Biodiversity occurrence data published by: Minnesota Biodiversity Atlas (accessed through the Minnesota Biodiversity Atlas Portal, bellatlas.umn.edu, 8/17/2025). |
|
| 8/17/2025 | ||
Occurrence |
||
|
||
Taxonomy |
|
Order |
Coleoptera (Beetles) |
Suborder |
Polyphaga (Water, Rove, Scarab, Long-horned, Leaf, and Snout Beetles) |
Infraorder |
Elateriformia |
Superfamily |
Buprestoidea |
Family |
Buprestidae (jewel beetles) |
Subfamily |
Agrilinae |
Tribe |
Agrilini |
Subtribe |
Agrilina |
Genus |
|
Subgenus |
|
Subordinate Taxa |
|
|
|
Synonyms |
|
|
|
Common Names |
|
dogwood agrilus dogwood cambium borer |
|
Glossary
Elytra
The hardened or leathery forewings of beetles used to protect the fragile hindwings, which are used for flying. Singular: elytron.
Pronotum
The exoskeletal plate on the upper side of the first segment of the thorax of an insect.
Visitor Photos |
||
Share your photo of this insect. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
Alfredo Colon |
 |
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
||
|
||
|
||

Slideshows |
|

Visitor Videos |
||
Share your video of this insect. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
Other Videos |
||
|

Created: 6/14/2018 Last Updated: © MinnesotaSeasons.com. All rights reserved. |