flatheaded poplar borer
(Dicerca tenebrica)
Conservation • Description • Habitat • Ecology • Distribution • Taxonomy
|
|
||||||||||||||
Description |
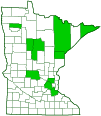
Flatheaded poplar borer is a medium-sized metallic wood-boring beetle. In North America it occurs in the east from Nova Scotia south to Massachusetts, west to southern Ontario and Minnesota. In the west it occurs from Alaska south to New Mexico, east to Manitoba and Nebraska. It is common, possibly the most frequently encountered Dicerca species in aspen forests. Adults are found from March to November in deciduous and mixed forests. They breed on a variety of trees in the genus Populus. In Minnesota these include bigtooth aspen and quaking aspen. In other areas their hosts include black cottonwood and narrow-leaf cottonwood. Adults feed on these and other Populus species, especially balsam poplar. They are sun loving, and can be seen sitting on logs, trunks, branches, or foliage of their host trees and other trees near their hosts. Adults are rigid and streamlined. The body is elongated, moderately convex, and broadly flattened. Females are 9⁄16″ to 1″ (14.5 to 26.0 mm) in length and 3⁄16″ to ⅜″ (4.5 to 9.0 mm) in width. Males are a little smaller, ⅝″ to ⅞″ (15.0 to 21.5 mm) in length and 3⁄16″ to ¼″ (4.8 to 7.2 mm) in width. The color of the upper side is variable, from brass-colored to black, sometimes with a bluish tint, and always with metallic reflections and heavy white or pale speckling. The underside is coppery and iridescent. The head is flattened. This is the feature that gives the species part of its common name. It is slightly impressed in the middle both on the top (vertex) and in front. The eyes are widely separated. The antennae are moderately slender and relatively short, reaching just to the middle of the plate on the upper side of the first segment of the thorax (pronotum). They have 11 segments. The fifth through eleventh segments are distinctly saw-toothed (serrate). The mouthparts are directed downward. The pronotum is wider than long. The sides are almost parallel in front, distinctly widened in the middle, and narrowest at the rear. The rear margin has two concave curves meeting in the middle in a convex curve. The surface is coarsely pitted (punctate). There is a distinct, coarsely punctate channel in the middle extending from the rear almost to the front margin, and a smooth raised area on each side of the channel. There is another slightly raised area halfway between the channel and the lateral margins. The plate between the wing bases (scutellum) is small, rounded, and visible. The wing covers (elytra) are wider at the base than the pronotum. They are almost parallel at the base, widest just beyond the middle, and strongly narrowed to the tip. They are distinctly grooved, especially toward the inner margin (suture). The tips are extended narrowly, stub-like, and are distinctly separated. The legs are moderately robust. On the male the fourth leg segment (tibia) has a single tooth on the underside. There is no similar tooth on the female. The last part of each leg (tarsus), corresponding to the foot, has 5 segments. There is a pair of claws at the tip of each tarsus. |
Size |
Male total length: ⅝″ to ⅞″ (15.0 to 21.5 mm) Female total length: 9⁄16″ to 1″ (14.5 to 26.0 mm) |
Similar Species |
Habitat |
Deciduous and mixed forests. |
Ecology |
Season |
March to November |
Behavior |
|
Life Cycle |
Eggs are laid in wounds, cracks, or crevices in the rough bark of branches and branch stubs that are exposed to sunlight. Larvae bore into the sapwood and heartwood of recently dead wood or in dead parts of living trees. They make large rather openings in the bark when they burrow into it. Development information for North American species is unknown, but this species probably spends three to seven years as larvae. Adults create large openings in the bark when they first emerge. They hibernate under loose bark in the winter. |
Larva Food |
Sapwood |
Adult Food |
Leaves of trees in the genus Populus, including |
Distribution |
||
|
Sources |
|
| 7/4/2024 | ||
Occurrence |
||
Common |
||
Taxonomy |
|
Order |
Coleoptera (Beetles) |
Suborder |
Polyphaga (Water, Rove, Scarab, Long-horned, Leaf, and Snout Beetles) |
Infraorder |
Elateriformia |
Superfamily |
Buprestoidea |
Family |
Buprestidae (jewel beetles) |
Subfamily |
Chrysochroinae |
Tribe |
Dicercini |
Subtribe |
Dicercina |
Genus |
Dicerca |
Subordinate Taxa |
|
|
|
Synonyms |
|
Buprestis tenebrica Dicerca prolongata Stenuris tenebrica |
|
Common Names |
|
flatheaded poplar borer poplar dicerca |
|
Glossary
Elytra
The hardened or leathery forewings of beetles used to protect the fragile hindwings, which are used for flying. Singular: elytron.
Pronotum
The exoskeletal plate on the upper side of the first segment of the thorax of an insect.
Scutellum
The exoskeletal plate covering the rearward (posterior) part of the middle segment of the thorax in some insects. In Coleoptera, Hemiptera, and Homoptera, the dorsal, often triangular plate behind the pronotum and between the bases of the front wings. In Diptera, the exoskeletal plate between the abdomen and the thorax.
Tarsus
On insects, the last two to five subdivisions of the leg, attached to the tibia; the foot. On spiders, the last segment of the leg. Plural: tarsi.
Tibia
The fourth segment of an insect leg, after the femur and before the tarsus (foot). The fifth segment of a spider leg or palp. Plural: tibiae.
Vertex
The upper surface of an insect’s head.
Visitor Photos |
||
Share your photo of this insect. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
Charlene |
||
 |
|
|
sitting on a plastic tarp in the sunshine |
|
|
Bill Reynolds |
||
 |
||
Metalic Wood-borer I don't see this beetle often, just time to time. This one is on an outdoor plastic storage box, thus the strange surface. Taken the image with phone, it just won't sit for a frontal shot. |
||
MinnesotaSeasons.com Photos |
||
|
||
|
||

Slideshows |
|

Visitor Videos |
||
Share your video of this insect. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
|
Other Videos |
||
|

Visitor Sightings |
||
Report a sighting of this insect. |
||
This button not working for you? |
||
Charlene |
Location: Fort Ripley, MN sitting on a plastic tarp in the sunshine |
 |
MinnesotaSeasons.com Sightings |
||
|

Created: 6/11/2023 Last Updated: © MinnesotaSeasons.com. All rights reserved. |